PMCTrack is an open-source OS-oriented performance monitoring tool for GNU/Linux. This performance tool has been specifically designed to aid kernel developers in implementing scheduling algorithms or resource-management strategies on Linux that leverage data from performance monitoring counters (PMCs) to perform optimizations at run time. Unlike other monitoring tools, PMCTrack features and in-kernel API enabling the OS scheduler to access per-thread PMC data in an architecture-independent fashion.
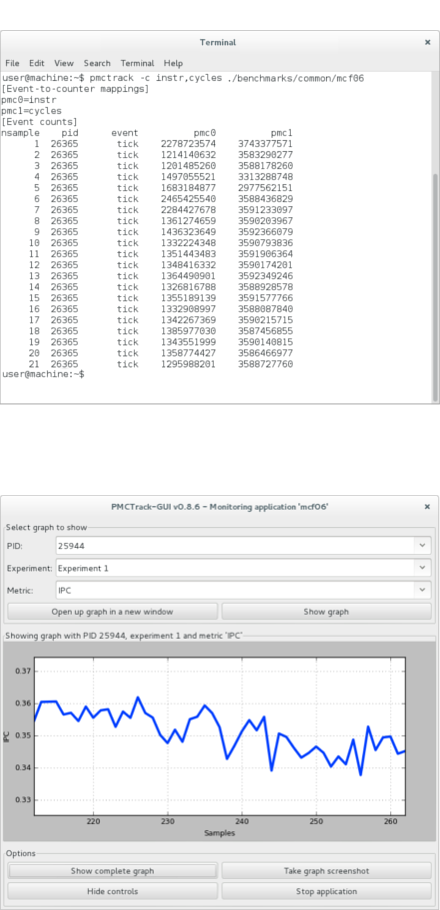
Despite being an OS-oriented tool, PMCTrack still allows the gathering of PMC values from user space, enabling kernel developers to carry out the necessary offline analysis and debugging to assist them during the scheduler design process. In addition, the tool provides both the scheduler and the userspace PMCTrack components with other insightful metrics available in modern processors that are not directly exposed as PMCs, such as cache occupancy or energy consumption.
OS-scheduler oriented
PMCTrack’s novelty lies in the monitoring module abstraction, an architecture-specific extension responsible for providing any OS scheduling algorithm that leverages PMC data with the performance metrics it requires to function. This abstraction makes it possible to implement architecture-independent OS scheduling algorithms.
Provides more data
Different metrics provided by modern hardware but not modeled directly via performance counters, such as power consumption or an application’s cache footprint, can be also exposed to the OS scheduler or to the user applications as PMCTrack’s virtual counters
Userspace tools
PMCTrack also enables to gather PMC data (or other data available in modern processors such as cache occupancy or energy consumption) from userspace by using the pmctrack command line tool, libpmctrack or PMCTrack-GUI.